
If only one specification is provided (unilateral) the use the value that involves that specification limit. Unlike Cp (and Pp), the Cpk (and Ppk) index can be calculated using unilateral or bilateral tolerances. This minimum value must be equal to or greater than the minimum acceptability level. Select the MINIMUM value as the Cpk and to serve as the baseline value. There are two calculations from the formula providing two values for Cpk. Cpk also requires input from the customer for the lower specification limit (LSL) and upper specification limit (USL). The Cpm capability calculation accounts for a nominal value. Cpk will never exceed the Cp Similar to Ppk, the Cpk capability index is only a function of the standard deviation and mean of the data, not a nominal (target) value that may be historical or provided by the customer. and since the maximum value for k is 1.0, then the value for Cpk is always equal to or less than Cp. Both Cpk and Ppk relate the standard deviation and centering of the process about the midpoint to the allowable tolerance specifications. A perfectly centered process will have Cp = Cpk. The minimum value of "k" is 0 and the maximum is 1.0.
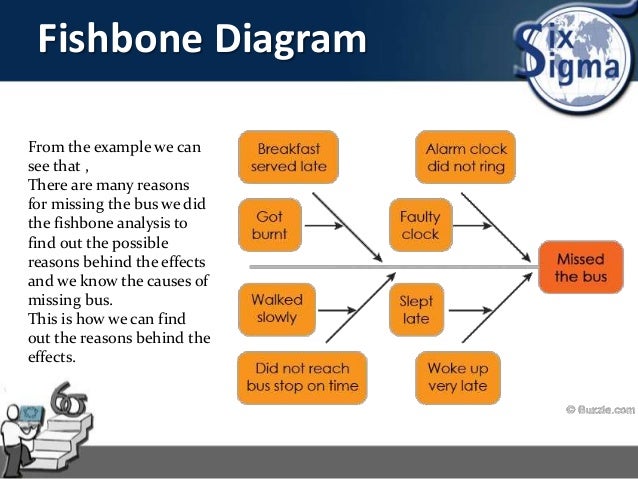
A perfectly centered process where the mean is the same as the midpoint will have a "k" value of 0. The addition of "k" in Cpk quantifies the amount of which a distribution is centered, in other words it accounts for shifting. The Cp is commonly referred to as the process entitlement because, when centered, it represents the best performance possible. The Cp is the best a process can perform if that process is centered on the midpoint. Think about it this way, if a subgroup size is 5 and all five data points show an average that is vastly different from the averages of the other subgroups (that also have 5 data points) then there is a strong chance that the subgroup was measured under a "unique" or special condition. The greater the subgroups size the higher likelihood the special cause variation is detected and that it exist if it is detected. It is recommended to have at least 25 subgroups and preferably each subgroup having >1 data point.

A process that performs at a 6 sigma level free#
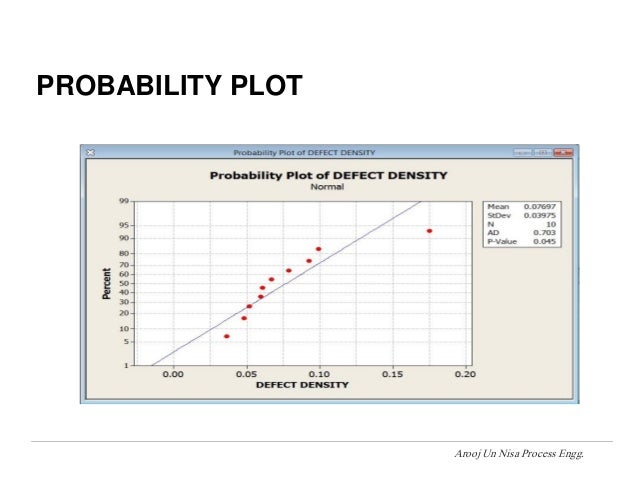
Use time-series charts and SPC charts to determine process control. This goes for the baseline measurement and the final measurement. This is called the baseline measurement.Īfter the improvements are done, the process is measured again and a new Cpk value is calculated in the CONTROL phase.Īs with all the process capability indices, the process must be in control before assessing capability. In order to measure improvement (or lack of) there must be a starting point. After the MSA is complete, the Six Sigma project has a goal of improving the baseline measurement. This requires the involvement and buy-in of all levels of the organization, from top management to front-line employees.īy implementing Six Sigma, organizations can improve their processes and increase efficiency, increasing customer satisfaction and profitability.NOTE: There are two values calculated and the minimum value (worst case) is used.Ĭpk is an option (along with z-score and PPM or DPMO) when describing process baseline measurement in the MEASURE phase. Six Sigma as a Philosophyįinally, when Six Sigma is used as a philosophy, it is integrated into the organization's overall culture to improve processes and achieve near-perfect performance continuously. Controls are put in place in the Control phase to ensure sustained improvements. In the Improve phase, changes are made to the process based on the analysis. The collected data is analyzed in the Analyze phase to understand the problem. In the Measure phase, the current performance is measured, and data is collected. In the Define phase, the problem is identified and defined. Using Six Sigma as a process involves using the DMAIC method, which consists of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. When it is used as a process, the focus shifts to improving processes and increasing efficiency. This level of deployment is typically the starting point for implementing Six Sigma. When Six Sigma is used as a tool, the focus is on reducing variation and bringing down the defect level to 3.4 defects per million opportunities ( DPMO).

In Six Sigma, there are three levels of deployment: as a statistical tool, as a process for improving processes, and as a philosophy in the organization.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
